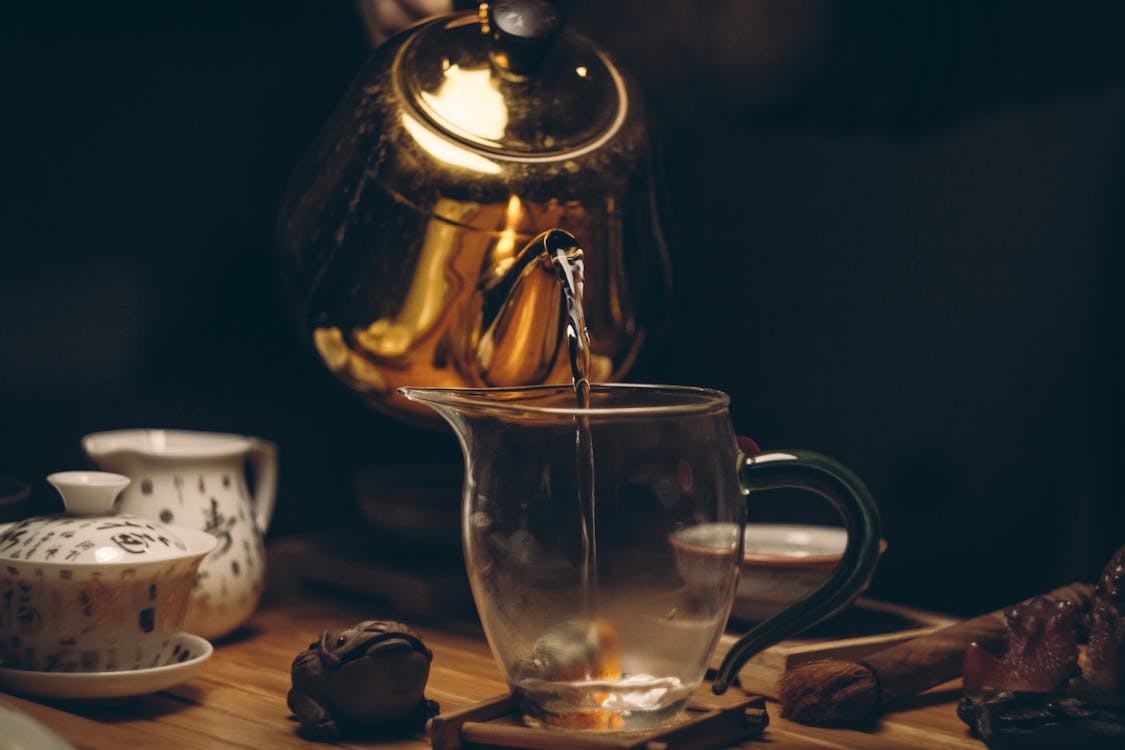
Making tea is a simple process, and there are various methods depending on the type of tea you’re preparing. Here’s a basic guide for making a standard cup of tea using loose tea leaves or tea bags:
Ingredients:
Water
Tea leaves or tea bags
Optional: Sweeteners (sugar, honey), milk, lemon, or other flavorings

Steps:
1. Boil Water:
Bring fresh, cold water to a boil. The amount of water will depend on how many cups of tea you want to make.
2. Preheat the Teapot or Teacup (Optional):
Pour a small amount of hot water into the teapot or teacup and swirl it around. This helps to warm the vessel, ensuring the tea stays hot.
3. Add Tea Leaves or Tea Bag:
If using loose tea leaves, measure the appropriate amount (usually 1 teaspoon per 8 ounces of water) and place them into a tea infuser or directly into the teapot.
If using tea bags, place the tea bag into the teapot or teacup.
4. Pour Hot Water:
Pour the hot water over the tea leaves or tea bag.
5. Steep the Tea:
Allow the tea to steep for the recommended time. The steeping time varies depending on the type of tea:
Black Tea: 3-5 minutes
Green Tea: 2-3 minutes
White Tea: 4-5 minutes
Herbal Tea: 5-7 minutes
Oversteeping can lead to a bitter taste, so it’s essential to follow the recommended steeping times.
6. Remove Tea Leaves or Tea Bag:
Once the tea has steeped, remove the tea leaves or tea bag to prevent over-brewing.
7. Optional Additions:
Add sweeteners (sugar, honey), milk, lemon, or any other flavorings according to your preference. Stir gently.
8. Enjoy:
Your tea is now ready to be enjoyed! Sip it slowly and savor the flavors.
Remember, the brewing time and water temperature can vary depending on the type of tea you’re preparing, so it’s a good idea to check the specific recommendations for the tea you have. Additionally, experimenting with tea-making allows you to find the perfect strength and flavor that suits your taste preferences.
Benefits of Tea

Tea, whether black, green, white, or herbal, is known for its numerous health benefits. Here are some of the potential benefits associated with regular tea consumption:
Antioxidant Properties:
Tea contains antioxidants, such as catechins and polyphenols, which help neutralize free radicals in the body. Antioxidants may contribute to overall health and play a role in preventing cell damage.
Heart Health:
Regular consumption of tea has been linked to a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. The antioxidants in tea may help improve heart health by reducing inflammation and improving blood vessel function.
Improved Mental Alertness:
Tea contains caffeine, which is a natural stimulant. Moderate caffeine intake from tea can enhance mental alertness, concentration, and mood without the jittery effects often associated with higher caffeine sources.
Weight Management:
Some studies suggest that the combination of caffeine and catechins in green tea may contribute to weight loss and fat burning by boosting metabolism and improving fat oxidation.
Oral Health:
Tea has natural antibacterial and antiviral properties that may help promote oral health by inhibiting the growth of bacteria in the mouth. Additionally, fluoride is found in tea, which is beneficial for dental health.
Reduced Cancer Risk:
The antioxidants in tea may have protective effects against certain types of cancers. Regular consumption of tea has been associated with a lower risk of developing certain cancers, although more research is needed in this area.
Bone Health:
Some studies suggest that tea consumption, particularly green tea, may contribute to improved bone health by enhancing bone mineral density.
Digestive Health:
Herbal teas, in particular, are known for their potential benefits in promoting digestive health. Peppermint tea, ginger tea, and chamomile tea, for example, are often used to relieve indigestion and ease stomach discomfort.
Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes:
Regular consumption of green tea has been linked to a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The polyphenols in green tea may help improve insulin sensitivity.
Hydration:
Tea is a good source of hydration, and drinking tea contributes to your daily fluid intake. While tea contains caffeine, it is generally less dehydrating than coffee.
It’s important to note that individual responses to tea can vary, and excessive consumption of certain types of tea, particularly those with high caffeine content, may have adverse effects. Additionally, the health benefits of tea are best achieved as part of a balanced and healthy lifestyle. If you have specific health concerns or conditions, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.